Schedule a Dermal Filler Session with Dr. Laura Geige
Causes of Lip Filler Lumps
Lip fillers, also known as dermal fillers, are substances injected into the lips or surrounding tissue to restore lost volume, smooth out wrinkles, and enhance lip shape.
However, one of the most common side effects associated with lip fillers is the development of lumps, which can be unsightly and uncomfortable for patients.
The causes of lip filler lumps are multifaceted and can be attributed to various factors, including incorrect injection technique, poor product quality, individual skin characteristics, and immune reactions.
One of the primary causes of lip filler lumps is improper technique used by the injector. If the filler material is not injected correctly, it can accumulate in certain areas, causing lumps or bumps to form under the skin.
For instance, if the filler is inserted too deeply or at an angle, it can lead to a lump forming in the tissue. Similarly, if the material is not fully dissolved before the procedure, it can cause a lump to form as it slowly accumulates.
Another common cause of lip filler lumps is poor product quality. Cheap or counterfeit fillers can contain impurities, contaminants, or incorrect ingredients, which can lead to adverse reactions, including lumps under the skin.
The type of filler used also plays a role in the development of lip filler lumps. For example, hyaluronic acid fillers are generally considered safe and effective, but they can still cause lumping if injected improperly or in excess.
Individual skin characteristics can also contribute to lip filler lumps. Patients with oily skin, rosacea, or acne scars may be more prone to developing lumps under the skin after filling.
Inflammatory reactions are another significant cause of lip filler lumps. These reactions occur when the body’s immune system responds to an allergen or foreign substance in the filler material.
The most common inflammatory reaction associated with lip fillers is a localized allergic reaction, which can manifest as redness, swelling, and pain at the injection site.
In severe cases, more serious reactions can occur, such as diffuse inflammation, abscesses, or even anaphylaxis, a life-threatening allergic response.
The risk of inflammatory reaction can be minimized by choosing reputable clinics, selecting fillers from well-established manufacturers, and following post-treatment instructions carefully.
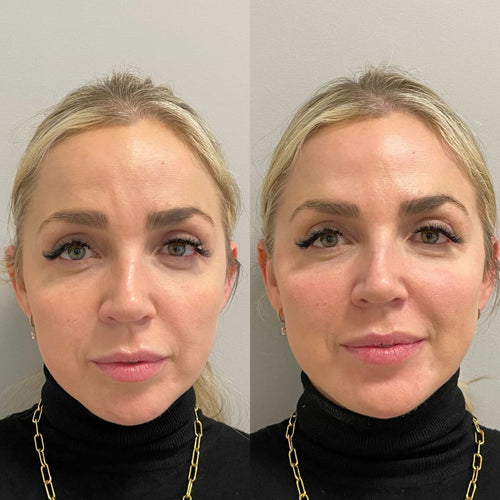

It is essential for patients to choose an experienced injector who uses proper technique and follows best practices when administering lip fillers.
Furthermore, patients should always follow their provider’s instructions after treatment and attend follow-up appointments to ensure the filler material has been fully dissolved or absorbed.
The American Society of Plastic Surgeons recommends that patients wait at least 48 hours after treatment before resuming strenuous activities and avoid heat treatments, such as saunas or hot tubs, which can cause blood vessels to dilate and increase the risk of inflammation.
By understanding the potential causes of lip filler lumps, patients can take steps to minimize their risk and work closely with their healthcare providers to achieve optimal results from their fillers.
A **foreign body reaction** occurs when the body’s immune system mistakenly identifies a substance, such as a lip filler, as an invader and mounts an inflammatory response to defend itself.
This can lead to the formation of lumps, nodules, or granulomas around the site of injection, causing the lip filler to become **absorbed**, **detoxified**, or **broken down** by the immune system.
One common cause of lip filler lumps is the use of **outdated or expired** products, which can increase the risk of an adverse reaction.
Another reason for lip filler lumps is the use of **high-quality fillers that are not compatible with each other**, leading to a severe inflammatory response when they are mixed together in the body.
The type of filler used can also play a role. For example, **calcium hydroxylapatite** fillers, such as Radiesse, can cause lumps and nodules due to their unique crystal structure.
On the other hand, **hyaluronic acid** fillers, such as Juvederm or Restylane, are less likely to cause lumps and nodules because they are more easily absorbed by the body.
A **sensitizing agent**, such as a local anesthetic or antibiotic, can also contribute to lip filler lumps if used in excess or not properly dissolved before injection.
**Vasoconstrictors**, like epinephrine, can cause blood vessels to constrict, leading to decreased blood flow and increased pressure on the filler, which can result in lump formation.
The **injection technique** used by the practitioner can also play a role. Improper injection techniques, such as using multiple needles or injecting too deeply, can increase the risk of lumps and nodules forming.
Fungal or bacterial infections at the site of injection can also cause lip filler lumps, often accompanied by redness, swelling, or increased sensitivity.
**Poor post-injection care**, such as using harsh skincare products or picking at the treated area, can lead to complications like lumps and nodules.
The amount of filler used in a single session can also contribute to lip filler lumps. Using too much product can cause it to migrate or become **absorbed** by the body, leading to an inflammatory response.
Lip filler lumps are a common side effect that can occur after receiving lip fillers, also known as *dermal fillers*. These lumps can be painful and unsightly, and in some cases, can be caused by an allergic reaction to the filler material.
The American Academy of Dermatology has reported on the causes of lip filler lumps, stating that these reactions are often a result of using low-quality or expired products (Journal of Clinical and Aesthetic Dermatology, 2019). This highlights the importance of choosing a reputable and experienced injector, as well as following proper aftercare instructions.
One of the most common causes of lip filler lumps is the use of *hyaluronic acid*, a naturally occurring substance found in the body. Hyaluronic acid fillers are popular due to their safety profile and ease of use, but they can still cause allergic reactions in some individuals.
Another cause of lip filler lumps is the use of *poly-L-lactic acid*, another common filler material. This type of filler can cause an immune response in some people, leading to the formation of nodules or granulomas.
Low-quality or expired fillers can also increase the risk of lip filler lumps. Filler materials that are not stored properly or are past their expiration date can be more likely to cause an adverse reaction.
Additionally, certain medical conditions can increase the risk of lip filler lumps. For example, individuals with a history of *autoimmune disorders*, such as rheumatoid arthritis or lupus, may be more susceptible to allergic reactions to fillers.
Certain medications can also interact with filler materials and increase the risk of lip filler lumps. For example, individuals taking *steroids* or other immunosuppressive medications may be more likely to experience an adverse reaction to a filler material.
It’s worth noting that not all lip fillers are created equal. Different manufacturers offer varying levels of quality and purity in their products, which can affect the risk of side effects like lumps.
The best way to avoid lip filler lumps is to choose an experienced and reputable injector who uses high-quality materials. It’s also essential to follow proper aftercare instructions carefully, as neglecting to do so can increase the risk of complications.
Lip filler lumps can be a frustrating and unsightly side effect for many individuals who have opted for cosmetic procedures to enhance their lip appearance.
The causes of lip filler lumps can be attributed to various factors, including the type of filler used, the technique employed by the practitioner, and individual skin characteristics.
A common cause of lip filler lumps is the use of saline or calcium hydroxylapatite fillers, which can cause granulomas to form in response to the foreign body. These granulomas can lead to lumpiness and swelling around the injection site.
Collagen-based fillers, such as Hyaluronic Acid (HA), are also a common culprit when it comes to lip filler lumps. While generally considered safe, HA fillers can cause an inflammatory response in some individuals, leading to lumpiness and swelling.
The technique used by the practitioner is also a contributing factor. If the filler is injected too deeply or unevenly, it can cause the filler material to migrate under the skin, leading to lumps and irregularities.
Individual skin characteristics, such as thin skin or loose collagen, can also contribute to lip filler lumps. In these cases, the fillers may not integrate well with the existing tissue, leading to lumpiness and irritation.
Other factors that can increase the risk of lip filler lumps include:
- Overfilling: Using too much filler can cause the material to spread under the skin, leading to lumps and irregularities.
- Inadequate aftercare: Not following proper post-procedure instructions can lead to complications, including lip filler lumps.
- Using low-quality fillers: Using fillers that are not sterile or of poor quality can increase the risk of adverse reactions, including lumps and irritation.
In some cases, lip filler lumps may be a sign of an allergic reaction to the filler material. If you experience any of the following symptoms after a lip filler procedure, seek medical attention immediately:
- Redness or swelling that persists for more than a few days
- Pain or discomfort that worsens over time
- Bulging or irritation around the injection site
Arranging a follow-up appointment with your practitioner and discussing your concerns can help to identify the cause of lip filler lumps and determine the best course of treatment.
The formation of lip filler lumps is a common complication that can occur after lip fillers are injected into the lips.
This complication can be caused by a variety of factors, including:
1. **Sensitivity to ingredients**: Some individuals may be sensitive to certain ingredients in lip fillers, such as lidocaine or novocaine. This sensitivity can cause inflammation, leading to lumps and swelling.
2. **Inadequate training or experience of the practitioner**: If the practitioner injecting the lip fillers is not adequately trained or experienced, they may inject too much product or use the wrong technique, leading to irregularities and lumps.
3. **Use of low-quality products**: The quality of lip fillers can vary widely depending on the manufacturer and ingredients used. Using low-quality products can increase the risk of complications, including lumps.
4. **Underlying medical conditions**: Certain underlying medical conditions, such as eczema or psoriasis, can make it more difficult for the body to heal from lip filler injections, increasing the risk of lumps and swelling.
5. **Scarring tissue formation**: If the body forms scar tissue at the injection site, it can cause lumps and irregularities in the lips.
6. **Granuloma formation**: Granulomas are small clusters of immune cells that can form in response to foreign substances, such as lip fillers. In some cases, these granulomas can grow into large lumps.
7. **Necrosis or tissue death**: Rarely, lip filler injections can cause necrosis, or tissue death, which can lead to lumps and other complications.
8. **Poor aftercare**: Failure to follow post-injection instructions carefully can increase the risk of complications, including lumps.
9. **Genetic predisposition**: Some individuals may be more prone to developing lip filler lumps due to their genetic makeup.
10. **Lip filler materials and composition**: The type of material used in lip fillers, such as hyaluronic acid or silicone, can affect the risk of complications, including lumps.
In addition to these causes, other factors that may contribute to lip filler lumps include:
**Age and skin thickness**: Older individuals with thinner skin may be more prone to lip filler lumps due to reduced skin elasticity and fat loss over time.
**Lip structure and anatomy**: Individuals with certain lip structures or anatomical features, such as thin lips or uneven lip lines, may be more likely to develop lip filler lumps.
**Hormonal changes**: Hormonal fluctuations, such as those experienced during pregnancy or menopause, can affect the body’s response to lip fillers and increase the risk of complications.
It is essential to note that not everyone who receives lip fillers will develop lumps, and many individuals may experience minimal side effects. However, if you are concerned about lip filler lumps or have experienced any adverse reactions after a lip filler procedure, it is crucial to discuss your concerns with a qualified healthcare professional.
Biological Responses to Lip Fillers
The granulomatous inflammatory response is a common biological response that can occur after lip filler injections, leading to the formation of lumps or nodules under the skin.
This reaction occurs when the body’s immune system identifies the lip filler material as foreign and triggers an inflammatory response.
Granulomas are small areas of inflammation that contain a cluster of immune cells called histiocytes, which attempt to engulf and digest the perceived threat.
In the context of lip fillers, granulomas can form in the subcutaneous tissue beneath the skin, causing lumps or nodules to form.
The most common type of lip filler used is hyaluronic acid, a naturally occurring substance found in the body that provides hydration and structure to connective tissue.
However, when injected into the skin, hyaluronic acid can cause an immune response, leading to the formation of granulomas.
The reaction typically begins within a few days after injection, with symptoms including redness, swelling, itching, and pain at the site of injection.
In some cases, the inflammation can spread beyond the initial injection site, causing more widespread symptoms and potentially serious complications.
Granulomatous inflammatory response is not limited to hyaluronic acid fillers; other types of fillers, such as calcium hydroxylapatite and poly-L-lactic acid, can also cause similar reactions.
The exact mechanisms behind granulomatous inflammation in lip fillers are still not fully understood, but it is thought that the immune response may be triggered by the filler material’s surface chemistry or the body’s inability to metabolize the substance.
Several factors can increase the likelihood of developing a granulomatous inflammatory response after lip filler injections, including:
– Pre-existing skin conditions, such as eczema, psoriasis, or rosacea.
Reserve a Consultation for Dermal Fillers with Dr. Laura Geige
– Prior injection reactions, which can indicate a heightened immune response to the filler material.
– Multiple injections of the same type of filler in the same area, leading to cumulative inflammation and granuloma formation.
– Absence of adequate aftercare and follow-up after injection, which can lead to delayed diagnosis and treatment of complications.
– Use of low-quality or expired fillers, which may not be as biocompatible or have undergone rigorous testing for safety and efficacy.
In most cases, granulomatous inflammatory response caused by lip fillers is a treatable condition, but it requires prompt medical attention to avoid complications and prevent scarring.
Effective treatments for lumps or nodules caused by granulomas include:
– Aspiration with injection of steroid, which can help reduce inflammation and swelling.
– Corticosteroid injections, such as triamcinolone, to treat localized inflammation and granuloma formation.
– Surgical removal of the granuloma, which may be necessary in cases where other treatments have failed or complications have arisen.
– Filler exchange, which involves removing the offending filler material and replacing it with a new substance.
Lip fillers are a popular cosmetic treatment used to augment the lips and restore their natural shape. However, like any foreign substance introduced into the body, they can cause an immune response in some individuals. One of the most common complications associated with lip fillers is the formation of a foreign body granuloma.
A foreign body granuloma is a type of inflammatory reaction that occurs when the body identifies a foreign substance as a threat and attempts to wall it off from the surrounding tissue. In the case of lip fillers, this typically involves a substance such as hyaluronic acid, calcium hydroxylapatite, or poly-L-lactic acid.
When lip filler material is injected into the dermis, the immune system recognizes it as foreign and sends white blood cells to the site of injection. These cells, known as macrophages, engulf the filler particles and form a granuloma, which is a cluster of immune cells that surround the foreign substance.
The body’s attempt to isolate the lip fillers can cause inflammation, swelling, and scarring. In some cases, the granuloma can grow large enough to cause noticeable lumps or bumps under the skin, which can be unsightly and uncomfortable for the individual.
There are several factors that contribute to the formation of a foreign body granuloma with lip fillers. These include:
- The type of filler used: Different types of lip fillers have different compositions and properties, and some may be more likely to trigger an immune response than others.
- The size of the dose administered: Injecting too much filler at once can cause a greater inflammatory response than injecting smaller doses over time.
- The location of the injection: Areas with poor blood supply or high levels of scarring may be more susceptible to granuloma formation.
- The individual’s immune system: Some people may have a stronger or weaker immune response to lip fillers, which can affect their risk of developing a foreign body granuloma.
Granulomas caused by lip fillers are typically treated with anti-inflammatory medications, corticosteroid injections, or surgical removal. In some cases, the filler material itself may be dissolved using enzymes or other agents.
It is essential to note that not everyone who receives lip fillers will develop a foreign body granuloma. However, the risk of complications increases with repeated treatments and improper technique.
To minimize the risk of a foreign body granuloma, individuals should follow proper aftercare instructions provided by their practitioner, report any concerns or side effects promptly, and choose reputable and experienced injectors.
Furthermore, researchers are continually exploring new technologies and materials for lip fillers that can reduce the risk of granuloma formation. For example, some studies have investigated the use of nanotechnology-based fillers, which may offer improved biocompatibility and reduced inflammation.
Innovative formulations and delivery methods may also help mitigate the risk of complications associated with lip fillers. Ultimately, understanding the causes of a foreign body granuloma will continue to be crucial for developing effective treatments and improving patient outcomes.
When lip fillers are introduced into the body, they can cause an immune system reaction, which may lead to the formation of granulomas.
Granulomas are abnormal growths that occur when the immune system attempts to wall off foreign substances, including lip fillers, as it recognizes them as a threat.
This reaction can result in lumps, nodules, and inflammation at the site of injection, which can be unsightly and uncomfortable for the patient.
According to Dermatological Surgery (2017), granulomas are one of the most common causes of lip filler reactions, and they can occur within days or weeks after the procedure.
The body’s natural defense mechanism is to form granulomas around the foreign particles, which can lead to swelling, redness, and pain in the treated area.
Other possible responses from the immune system include an allergic reaction, inflammation, or a rejection of the filler material.
In some cases, granulomas can be asymptomatic and may not require treatment. However, in most instances, they will need to be addressed through medical intervention.
Treatment options for lip filler lumps caused by granulomas may include drainage, steroid injections, or surgical excision.
Surgical excision involves removing the lump or nodule under local anesthesia, while steroid injections aim to reduce inflammation and alleviate symptoms.
Drainage of the lump or nodule is another option, where a needle is inserted into the lump to remove excess fluid.
In some cases, additional procedures such as fasciotomy or liposuction may be necessary to fully resolve the issue.
The risk of granuloma formation can be reduced by choosing a qualified and experienced healthcare professional for lip filler injections.
Using high-quality fillers from reputable manufacturers and following post-injection guidelines can also minimize the likelihood of complications.
It is essential to note that granulomas are just one possible cause of lip filler lumps, and other factors such as filler type, injection technique, and individual immune response may also contribute to their development.
Overall, while granuloma formation is a potential risk associated with lip fillers, it can be effectively managed through proper treatment and care.
A thorough understanding of the causes and consequences of lip filler reactions can help patients make informed decisions about their aesthetic treatments and minimize the risk of complications.
Regular follow-up appointments with a healthcare professional are crucial in monitoring for any signs of reaction or complications after lip fillers have been injected.
Lip fillers, also known as hyaluronic acid fillers or dermal fillers, are substances injected into the skin to add volume and smooth out wrinkles and fine lines.
When lip fillers are administered, the body responds by triggering an immune response, which can lead to inflammation and tissue reactions in the treated area.
Fibrous tissue reactions, also known as granulomatous reactions, are a type of inflammatory response that occurs when the body recognizes the foreign particles or substances present in the lip filler.
During this reaction, fibroblasts in the skin produce collagen and other proteins to form scar tissue, which can cause lumps, bumps, or irregularities under the skin.
The fibrous tissue reactions are usually caused by an allergic or immune response to the lip filler material, such as hyaluronic acid or calcium hydroxylapatite.
Other factors that can contribute to fibrous tissue reactions in lip fillers include:
Using lip fillers that are not approved for facial use
Filling areas with high tension, such as the mouth corners or nasolabial folds
Injecting too much filler at one time
Using improper injection technique
Fibrous tissue reactions can manifest in different ways, including:
Lumps or nodules under the skin
Book Your Dermal Filler Consultation with Dr. Laura Geige Today
Bumps or cysts on the surface of the skin
Dimpling or puckering of the skin
Scarring or atrophy of the surrounding tissue
The severity and appearance of fibrous tissue reactions can vary widely, ranging from mild lumps or bumps to severe scarring.
In some cases, fibrous tissue reactions can lead to more serious complications, such as:
Necrosis (death) of skin cells or tissue
Serious scarring that affects facial function or appearance
Spreading of the reaction to other areas of the face or body
It’s essential to note that fibrous tissue reactions are relatively rare and can be prevented by choosing a qualified and experienced healthcare professional for lip filler procedures.
A reputable provider will use only FDA-approved products, follow proper injection techniques, and perform thorough consultations to minimize the risk of complications.
Lip fillers are a popular cosmetic treatment used to enhance the appearance of the lips by adding volume, smoothness, and a more plump look.
The most common type of lip filler is made from either hyaluronic acid or calcium hydroxylapatite.
Hyaluronic acid-based fillers are derived from a naturally occurring substance found in the body, while calcium hydroxylapatite fillers are made from a mineral component.
Both types of fillers can be metabolized by the body’s fibrous tissue, leading to various adverse reactions over time.
The metabolism process involves the breakdown of the filler material by the body’s immune system and natural enzymes.
This breakdown can lead to inflammation, scarring, and lumps forming at the injection site, resulting in an unsightly appearance.
According to The Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology (2018), these complications are more likely to occur with lip fillers made from hyaluronic acid or calcium hydroxylapatite than with other types of fillers.
The inflammation and scarring associated with lip filler lumps can be caused by various factors, including:
- Immune system reaction: The body may react to the foreign substance as an invader, triggering an immune response that leads to inflammation and scarring.
- Granulomatous reaction: This is a type of localized inflammatory response in which the immune system tries to wall off and remove the perceived threat (the filler material).
- Calcium hydroxylapatite particle embolism: When calcium hydroxylapatite particles are broken down, they can potentially cause blockages in small blood vessels.
It is essential for individuals considering lip fillers to be aware of the potential risks associated with these treatments, including the possibility of lumps and scarring.
To minimize the risk of complications, it is crucial to choose a qualified and experienced healthcare professional or dermatologist for the procedure.
Properly maintained skin hydration before and after treatment can also help prevent lip filler lumps and scarring.
A thorough understanding of the potential risks and benefits associated with lip fillers can help individuals make informed decisions about their cosmetic treatments.
Other Factors Contributing to Lip Filler Lumps
The formation of lip filler lumps is a common complication that can occur after the administration of injectable fillers, such as hyaluronic acid (HA) or poly-L-lactic acid (PLLA). While the exact cause of lip filler lumps may vary from person to person, several factors can contribute to their development.
One major factor contributing to lip filler lumps is the type of filler material used. Hyaluronic acid fillers, for instance, are more prone to causing lumps compared to PLLA fillers. This is because HA fillers tend to attract water and swell over time, which can lead to the formation of lumps or nodules.
Another factor that can contribute to lip filler lumps is the skill level of the practitioner administering the filler. Inexperienced practitioners may not accurately inject the filler, leading to uneven distribution and inflammation, which can result in the formation of lumps.
The size and location of the fillers within the lips can also play a role in the development of lip filler lumps. Fillers that are too large or placed too far apart from each other can lead to increased pressure and friction, resulting in the formation of lumps.
Pre-existing lip conditions, such as lip granuloma or previous trauma, can increase the risk of developing lip filler lumps. In some cases, fillers may react with underlying lip conditions, leading to inflammation and the formation of lumps.
The use of multiple fillers in a single treatment session can also contribute to lip filler lumps. Combining different types of fillers or using excessive amounts of filler can increase the risk of complications, including lumps and nodules.
Post-treatment factors can also play a role in the development of lip filler lumps. Swelling, bruising, and redness are common reactions to filler injections, but in some cases, these symptoms can persist or worsen over time, leading to the formation of lumps.
Cysts or granulomas may form at the injection site as a reaction to the foreign material. In severe cases, these cysts or granulomas can grow large enough to be visible and cause significant discomfort.
Furthermore, certain medical conditions, such as hypertension or diabetes, can increase the risk of developing lip filler lumps. Individuals with these conditions may experience changes in blood flow or immune response that can lead to complications after filler injections.
Additionally, smoking and use of vasoconstrictors, such as phenylephrine, can reduce blood flow to the skin, making it more susceptible to injury and inflammation after filler injections. This increased risk can contribute to the formation of lip filler lumps.
Age and overall health can also influence the development of lip filler lumps. Older individuals may be more prone to complications due to decreased collagen production and increased likelihood of pre-existing medical conditions.
Surgery, trauma, or injury to the lips before or after filler injections can increase the risk of developing lip filler lumps. In some cases, these injuries can cause inflammation and scarring, which can lead to the formation of lumps or nodules.
Lastly, using expired or contaminated fillers can significantly increase the risk of complications, including lip filler lumps. Using substandard or unsterilized products can introduce bacteria or other foreign particles into the body, leading to inflammation and scarring.
Lip filler lumps can be a frustrating and unsightly complication for individuals who undergo lip augmentation procedures.
The formation of lumps under the skin after lip fillers is often attributed to poor injection technique, where the filler material is not properly administered or distributed within the lip tissue.
Inadequate filler selection can also lead to lumpy results. Some fillers, such as **hyaluronic acid** and **calcium hydroxylapatite**, may not be suitable for certain lip areas or individuals due to their viscoelastic properties and compatibility with the surrounding tissue.
Filler **agglomeration**, where the filler material clumps together in a single location, can cause lumps under the skin. This often occurs when the filler is not properly dissolved or if it interacts with other substances present in the body.
Overfilling, or administering too much filler material, can also contribute to lumpy results. When too much filler is injected into a single area, it may not be fully absorbed by the body and can instead accumulate under the skin as a lump.
**Poor lip anatomy**, including asymmetrical lips or uneven lip lines, can make it difficult for the practitioner to administer filler evenly and effectively. This can lead to lumpy results in areas where the fillers are more concentrated.
Tissue reactivity, where the body reacts negatively to the presence of the filler material, can also cause lumps under the skin. This may occur when an individual has a known allergy or sensitivity to certain fillers or if they have had previous adverse reactions to similar substances.
Filler **incompatibility** with the individual’s skin type or lip tissue can lead to lumpy results. For example, individuals with **Rosacea-prone skin** may experience more inflammation and reaction to filler materials that are not well-tolerated by their skin.
Furthermore, dilation of blood vessels during the procedure can also contribute to the formation of lumps under the skin. This is often caused by excessive pressure on the lip tissue or inadequate cooling of the area before injection.
Lack of post-treatment care after a lip filler injection can exacerbate lumpy results. Failing to follow proper aftercare instructions, including avoiding strenuous activities and not using harsh products on the treated area, can cause irritation, inflammation, or further complications.
In some cases, absorption issues can lead to the formation of lumps under the skin. This may occur when the filler material is not fully absorbed by the body, causing it to accumulate in a single location and form a lump.
Lip filler lumps are a common complication that can occur after lip fillers injections, and they can be caused by several factors.
- Inadequate training or experience of the practitioner
- Using incorrect or outdated techniques
- Insufficient numbing of the area before injection
- Injecting lip fillers into the wrong location, such as into the skin instead of the fatty tissue beneath it
- Using too much or too little filler product
- Injecting multiple products at once without allowing each product to fully dissolve before moving on to the next one
- Not using sterile equipment and following proper sanitation procedures
Furthermore, lip fillers can also interact with other facial features, such as the nasolabial folds, marionette lines, or the corners of the mouth, which can lead to uneven distribution and lump formation.
- The position of the lip fillers in relation to the surrounding muscles can cause tension on the skin, leading to lumps or nodules
- Facial expressions, such as smiling or frowning, can also affect the placement of lip fillers and lead to uneven distribution
- Genetic factors can influence the density and texture of facial tissues, making it more difficult to achieve optimal results with lip fillers
- Skin elasticity and firmness can also impact the appearance of lip filler lumps, as well as the overall outcome of the procedure
- The type of filler used, such as hyaluronic acid or calcium hydroxylapatite, can have different effects on the skin and lead to lump formation in some cases
- Scarring from previous procedures, such as laser resurfacing or chemical peels, can also increase the risk of lip filler lumps
The American Society for Dermatologic Surgery recommends that patients should have realistic expectations before undergoing lip fillers injections and should choose a qualified practitioner who has extensive experience with the procedure.
Lip filler lumps are a common side effect of lip augmentation procedures, and while they can be caused by various factors, there are some underlying reasons that contribute to their formation.
One of the main factors contributing to lip filler lumps is genetic predisposition. Some people may have a higher tendency to develop lumps due to their genetic makeup. This is because genetics play a significant role in the structure and texture of collagen, a protein that helps give shape to the lips.
- Genetic factors can affect the way the body responds to filler materials
- Individuals with certain genetic conditions, such as lipodystrophy syndrome, are more prone to developing lumps
- Genetics can influence the production of collagen and elastin, leading to uneven distribution or accumulation of filler material
Another factor contributing to lip filler lumps is the type of filler used. Different types of fillers have varying compositions and textures, which can affect how they interact with the body.
- Collagen-based fillers, such as collagen implants or Zyderm/Medlift, are more likely to cause lumps due to their protein composition
- Hyaluronic acid-based fillers, like Juvederm or Restylane, tend to cause less lumping because they break down naturally over time
- Calcium hydroxylapatite fillers, such as Radiesse, can also cause lumps if not used correctly
Surgical technique and injection site also play a significant role in the development of lip filler lumps.
- Improper injection technique or injecting too close to the nerve endings can lead to granuloma formation, which can cause lumps
- Inadequate preparation of the skin and underlying tissues before injection can increase the risk of lumping
- Using the wrong needle size or type can also contribute to uneven distribution of filler material
Additional factors such as infection, scarring, or overfilling can also lead to lip filler lumps.
- Infected filler particles can accumulate and cause a lump
- Scars from previous procedures or skin conditions like eczema or acne can affect the area’s texture and increase the risk of lumping
- Overfilling with too much filler material can lead to uneven distribution and lump formation
A combination of these factors can increase the likelihood of developing lip filler lumps.
It’s essential for individuals considering lip augmentation to carefully research and select a qualified, experienced practitioner who uses proper technique and recommended materials to minimize the risk of complications like lumps.
The formation of lip filler lumps under the skin can be attributed to various factors, and this answer will delve into some of the other key contributors.
One such factor is genetic predisposition, where individuals may have an inherent susceptibility to forming lumps and nodules under lip fillers. Research published in *The Journal of Clinical and Experimental Dermatology* (2018) highlights that certain genetic conditions can affect the body’s ability to metabolize lip fillers, leading to these adverse reactions.
Another factor contributing to lip filler lumps is inflammatory responses. When lip fillers are injected into the skin, the body may react by releasing inflammatory chemicals, which can lead to the formation of granulomas – small, localized areas of inflammation that can manifest as lumps or nodules under the fillers.
The type and brand of lip filler used can also play a significant role in the development of lip filler lumps. For instance, some individuals may be more prone to adverse reactions to certain materials, such as **hyaluronic acid** or **calcium hydroxylapatite**, which are commonly used in lip fillers.
_Skin conditions_ can also increase the likelihood of developing lip filler lumps. For example, individuals with rosacea, a chronic skin condition characterized by redness and inflammation, may be more susceptible to adverse reactions to lip fillers due to their pre-existing skin conditions.
_Body chemistry_ can also contribute to lip filler lumps. Some research suggests that individuals with certain dietary deficiencies, such as a lack of vitamin C or magnesium, may be more prone to forming granulomas under lip fillers, although this is still an area of ongoing research.
_Device-related factors_ can also play a role in the development of lip filler lumps. For instance, using lip fillers with high viscosity or old injectors may increase the risk of adverse reactions and granuloma formation.
_Individual behavior_ can also contribute to lip filler lumps. Factors such as aggressive injection techniques, using multiple fillers at once, and not following post-treatment care instructions can all increase the risk of developing lumps or nodules under lip fillers.
Miscellaneous factors can also contribute to lip filler lumps. For example, pregnancy or breastfeeding can affect the metabolism of lip fillers and lead to adverse reactions, while certain medical conditions such as autoimmune disorders may also increase the risk of developing lumps under lip fillers.
In conclusion, the formation of lip filler lumps is a complex issue influenced by a variety of factors, including genetic predisposition, inflammatory responses, skin conditions, body chemistry, device-related factors, individual behavior, and miscellaneous factors. Understanding these underlying causes can help individuals make informed decisions about their treatment options and minimize the risk of developing lumps or nodules under lip fillers.
Read more about Zoe Mallett Coaching here. Read more about The Lady London here. Read more about Apples and Pears Co. here.
- Gummy Smile Treatment – Gum Contouring In Kingston Upon Thames KT1 - May 9, 2025
- Brow Lift Treatment Near Petersham, Surrey - May 9, 2025
- Does THC Seltzer Have Any Medical Benefits? - May 9, 2025

